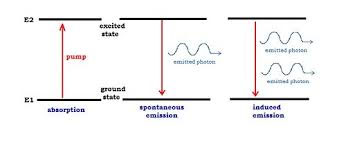
From the theory of interaction of radiation with matter, we can get an idea regarding the working of laser. Consider an atom that has only two energy levels, E1 and E2. When it is exposed to radiation having a stream of photons each energy hν, three distinct processes can take place.
- Absorption
- Spontaneous emission
- Stimulated emission
Absorption
An atom or molecule in the ground state E1 can absorb a photon of energy hν and go to the higher energy state E2. This process is known as absorption.
Spontaneous emission
The atom or molecule in the higher energy state E2 eventually return to the ground state by emitting their excess energy spontaneously.
Stimulated emission
A photon having energy E equal to the difference between the two levels E2 and E1 stimulate an atom in the higher state to make a transition to the lower state with creation of a second photon In order to achieve stimulated emission artificial condition known as population inversion is required.
Population inversion
Usually the number of particles more in higher energy level than the number of particles in lower energy level is called as population inversion.
Active system
A system in which the population inversion is achieved is called an active system
Pumping
The method of raising the particle from lower energy state to higher energy state is called as pumping.
Optical pumping
A more common method of pumping is optical pumping.
